The WinBlog
AI for business development #11 - Overcome AI challenges
Artificial Intelligence (AI) isn't just for tech giants. SMEs across industries are beginning to harness AI to
streamline operations, improve customer experience, and gain a competitive edge. But the road to adoption
isn’t always smooth.
In this blog, we highlight the most common challenges SMEs face when implementing AI — and more
importantly, how to overcome them.
Good news! With the right approach, AI is more accessible than ever. Let’s explore how.
CHALLENGE 1 - LIMITED BUDGET
Many SMEs assume that AI solutions are too expensive to consider.
- Start with affordable, cloud-based AI tools like Google AutoML, ChatGPT, or Microsoft Power Platform.
- Identify one or two high-impact use cases -e.g. automating customer support, lead scoring, or inventory forecasting.
- Consider AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS) models that avoid large upfront costs.
✅ Think ROI, not just expense.
CHALLENGE 2 - LACK OF IN-HOUSE EXPERTISE
Most SMEs don’t have data scientists or machine learning engineers on staff.
- Leverage no-code/low-code platforms to build AI models without programming skills.
- Collaborate with freelance consultants, universities, or incubators.
- Upskill your current team via affordable courses on platforms like Coursera or LinkedIn
Learning.
✅ You don’t need an AI lab—just a willingness to learn.
CHALLENGE 3 - POOR DATA QUALITY OR AVAILABILITY
AI requires good data—but many SMEs have messy, incomplete, or siloed data.
- Start with clean, structured data sources like CRM, sales, or website analytics.
- Use tools with automated data-cleaning features.
- Begin cultivating a company-wide culture of data ownership and integrity.
✅ Good data = good results.
CHALLENGE 4 - INTEGRATION WITH EXISTING SYSTEMS
Legacy systems, spreadsheets, or incompatible platforms can hinder AI implementation.
- Choose AI tools that offer plug-and-play integrations or open APIs.
- Prioritise solutions compatible with your tech stack -e.g. Salesforce, Xero, Shopify.
- Consult IT partners to support phased integration.
✅ AI should work with your business—not against it.
CHALLENGE 5 - UNCLEAR ROI
Without a clear way to measure success, it’s hard to justify investment.
- Define measurable KPIs tied to business outcomes -e.g., time saved, lead conversion rate,
reduced churn. - Pilot small AI projects and track improvements.
- Use those results to build a case for scaling.
✅ Small wins lead to big impact.
CHALLENGE 6 - RESISTANCE TO CHANGE
Staff may fear that AI will replace them or disrupt their roles.
- Involve employees early in the AI journey—get their input and feedback.
- Clearly communicate the goal: AI is here to assist, not replace.
- Offer training and support to help them adapt and grow alongside AI.
✅ Empowered teams = successful adoption.
CHALLENGE 7 - SECURITY & COMPLIANCE
Data privacy regulations like GDPR raise valid concerns around AI.
- Use tools with strong security credentials and compliance features.
- Store and process only the data you need.
- Consult legal or data protection experts before deploying customer-facing AI solutions.
✅ Security builds trust—internally and externally.
CHALLENGE 8 - VENDOR OVERLOAD & AI HYPE
With so many AI tools on the market, it’s hard to know what’s real and what’s fluff.
- Stay focused on solving specific business problems, not chasing buzzwords.
- Ask potential vendors for use cases, testimonials, or demos.
- Run a time-boxed pilot with clear success criteria.
✅ Start with strategy, not software.
STRATEGY RECAP - YOUR AI PLAYBOOK
Here’s a simplified plan SMEs can follow:
- Start small with one business use case
- Use what you have (existing data, cloud tools)
- Run a short pilot, measure success
- Scale up what works
- Involve your team every step of the way
✅ Smart AI adoption is iterative, not instant.
GETTING STARTED TODAY - A SIMPLE 4-STEP PLAN
- Identify a process that’s repetitive or data-heavy
- Explore one AI tool that fits your need
- Design a 90-day pilot
- Measure, adjust, scale
🛠️ You don’t need perfection—you need momentum.
FUTURE-PROOFING YOUR BUSINESS WITH AI
AI isn’t just a short-term fix—it’s a strategic investment.
- Stay curious about new tools
- Build AI literacy in your team
- View AI as a capability, not just a tool
🔮 Early adopters will lead tomorrow’s markets.
FINAL THOUGHTS – YOUR AI JOURNEY STARTS HERE
- Adopting AI can feel daunting—but it doesn’t need to be.
- You don’t need to be perfect. You just need to begin.
- With the right mindset, tools, and team engagement, AI can transform your SME.
🚀 You’ve got this.
AI for business development #10 - Steps to implement your AI
An effective AI strategy shall align with business goals and objectives, ensuring the technology
meets the organisation’s needs and seamlessly integrates with the people who will use it.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to transform businesses by improving efficiency,
enhancing customer experience, and creating new opportunities. However, without a clear AI
strategy aligned with business objectives, organisations may struggle to achieve meaningful results.
The following provides a roadmap to developing an effective AI strategy that ensures successful
implementation and long-term value.
ESTABLISH A CLEAR STRATEGY
AI must align with your organisation’s goals. Here are points to consider to build a structured AI
strategy.
- Understand your business goals
Determine how AI can support these goals, whether it's improving efficiency and reducing
costs, driving revenue growth, enhancing customer experience, enabling new business
models, innovating, and/or gaining a competitive edge.
- Define key performance indicators (KPIs)
Establish measurable goals to track AI success -e.g. revenue growth from AI-driven
automation, reduction in operational costs, customer satisfaction and engagement scores,
increased process efficiency, innovation impact
- Identify AI opportunities
Explore AI use cases tailored to your business needs. Prioritise initiatives that solve pressing
business challenges, provide high ROI, align with business strategy and resources, drive
innovation in products and services.
- Evaluate technical requirements
Assess your organisation’s AI readiness by evaluating existing infrastructure, determining
data availability and quality, understanding AI talent and expertise needs and exploring AI
integration with existing digital transformation efforts.
- Develop an implementation roadmap
Plan a phased AI adoption approach, setting clear milestones for proof of concept,
small-scale deployment, organisation-wide integration or scaling AI-driven innovation.
- Allocate resources
Ensure adequate funding, talent, and technology resources. Consider partnerships with AI
vendors or consultants if internal expertise is limited. For instance, collaborating with AI
service providers can accelerate implementation.
- Implement AI with ethical considerations
Monitor progress against KPIs and adjust your strategy when relevant. Monitor AI
deployment to ensure compliance with data privacy regulations, transparency and fairness
in AI decisions, bias mitigation in AI models, ethical use of AI in innovation.
THE FOUR PILLARS OF AN AI STRATEGY
These four pillars provide a structured approach to integrating AI into your organisation.
1. Vision - AI has the potential to drive business growth by many means -e.g. increasing revenue through data-driven insights and automation, enhancing customer engagement with personalised experiences, reducing operational costs by automating repetitive tasks, boosting productivity by optimising workflows and decision-making. Develop you own vision.
2. Value - to unlock the true value of AI, organisations must take a holistic approach by:
- Assessing the business impact beyond immediate cost savings.
- Evaluating risks, investment priorities, and workforce readiness.
- Preparing for potential disruptions to existing business models.
- Aligning AI implementation with long-term strategic objectives.
3. Adoption with key considerations to include:
- Defining the problem: what challenge is AI solving?
- Identifying stakeholders: who will be the primary users of this technology?
- Integration into business processes: where and how will AI be implemented?
- Expert involvement: which subject matter experts can support development?
- Measuring success: how will the impact of AI be evaluated?
- Sustaining value: how will the AI system be monitored and maintained over time?
- Ownership: who will be responsible for AI oversight and governance?
4. Risks - AI implementation comes with strategic risks that can hinder business success, such as:
- Ethical concerns, including bias and transparency.
- Compliance with regulatory frameworks and data privacy laws.
- Security threats from AI-driven automation and cyber risks.
- Organisational resistance to AI adoption and workforce displacement.
- Potential disruptions that could affect long-term business continuity.
A successful AI strategy requires a balanced approach, leveraging AI's potential while mitigating associated risks and ensuring alignment with business goals.
EXPERIMENT FIRST
Jumping into a full-scale AI strategy without first testing its core techniques can be premature. Instead, follow these five steps to introduce AI effectively:
1️⃣ Identify use cases – develop a portfolio of impactful, measurable, and quickly implementable AI applications.
2️⃣ Build the right skills – assemble a team with the necessary expertise to support AI initiatives.
3️⃣ Collect relevant data – gather and refine data essential for training and optimising AI models.
4️⃣ Choose the right technology – select AI techniques that align with the identified use cases, available skills, and data resources.
5️⃣ Establish organisational readiness – structure AI knowledge and expertise to ensure smooth integration and scalability.
This structured approach provides a fast-track introduction to AI, focusing on immediate results rather than a long-term strategic commitment. It ensures businesses gain practical insights before expanding AI adoption.
AI for business development #9 - The rise of AI agents
AI agents are no longer a futuristic concept—they are actively transforming industries, automating
processes, and enhancing efficiency. From customer service to sales automation, these intelligent
systems are reshaping how businesses operate.
But what exactly are AI agents, and how can they benefit your organisation?
WHAT ARE AI AGENTS?
An AI agent is an autonomous system designed to perform tasks, make decisions, and
interact with users or other systems. These agents leverage artificial intelligence (AI), machine
learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP) to comprehend, analyse, and act on data
with minimal human intervention.
AI agents extend beyond basic automation by incorporating decision-making and problem-solving
capabilities. They can interact with external environments, execute complex tasks, and adapt
their actions based on evolving data. Common applications include software development, IT
automation, code generation, and conversational AI assistants.
Unlike conventional software, AI agents operate as rational agents, meaning they perceive
their environment, process information, and act to achieve optimal outcomes. For example, a
robotic agent gathers sensor data, while a chatbot processes customer queries, applying AI
models to determine the best responses and next steps.
TYPES OF AI AGENTS
- Simple Reflex Agents act based solely on current input without considering history or future
outcomes (e.g., a thermostat adjusting temperature based on real-time data).
- Model-Based Reflex Agents maintain an internal model of the environment to make more
informed decisions (e.g., self-driving cars using traffic patterns and road maps).
- Goal-Based Agents plan actions to achieve predefined objectives (e.g., delivery robots
navigating optimal routes).
- Utility-Based Agents weigh multiple factors to determine the best course of action
(e.g., investment algorithms balancing risk and return).
- Learning Agents improve over time using feedback and past experiences (e.g., e-commerce
recommendation engines adjusting based on user behaviour).
- Hierarchical Agents operate with multi-level decision-making structures (e.g., robots
where high-level AI manages tasks and lower-level AI handles movement control).
- Multi-Agent Systems (MAS): networks of AI agents working collaboratively (e.g., intelligent
traffic management systems where vehicles communicate to optimise flow).
Understanding these categories helps businesses select the right AI agents for their specific needs.
KEY BENEFITS OF AI AGENTS
- Enhanced productivity: AI automates repetitive tasks, allowing teams to focus on strategic or creative initiatives.
- Cost efficiency: Reduces manual errors, optimises processes, and eliminates inefficiencies, lowering operational costs.
- Informed decision-making: AI-powered analytics process vast amounts of data, providing actionable insights for business strategies.
- Improved customer experience: Personalised interactions, fast responses, and adaptive recommendations drive engagement and satisfaction.
HOW EASY IS IT TO BUILD AN AI AGENT?
Developing AI agents has become increasingly accessible due to advancements in AI frameworks and automation tools. Businesses can integrate AI without deep technical expertise using pre-built solutions such as OpenAI’s GPT, Google’s Dialogflow, and Microsoft Azure AI.
Several no-code and low-code platforms enable AI agent development without extensive programming knowledge, including:
- Bubble: Enables AI-powered web applications with a visual interface.
- Zapier: Connects AI agents to various business applications for workflow automation.
- Make (formerly Integromat): Automates processes by linking AI services across platforms.
- Microsoft Power Automate: Integrates AI functionalities into business workflows with minimal coding.
- Chatfuel & ManyChat: Simplifies chatbot creation for Messenger, WhatsApp, and other messaging apps.
- Google AutoML: Provides AI model training with a low-code approach.
These tools empower businesses to deploy AI-driven solutions quickly, reducing development costs and improving operational efficiency.
HOW TO IMPLEMENT AI AGENT IN YOUR BUSINESS
- Identify Business Needs: determine where AI can add the most value.
- Choose the right technology: select AI tools suited to your industry and goals.
- Train & Integrate: seamlessly incorporate AI agents into existing systems.
- Monitor & Optimise: continuously refine AI models based on real-world performance.
THE FUTURE OF AI AGENTS
AI agents continue to evolve with advancements in deep learning, generative AI, and autonomous decision-making. Businesses that adopt AI-driven
automation today will gain a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Stay Ahead with AI. Ready to explore AI-powered solutions for your business? Contact us today for tailored AI integration strategies.
Stay tuned for more insights on AI, automation, and digital transformation!
AI for business development #8 - Why is AI now affordable?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer the exclusive domain of large corporations with deep pockets. In recent years, advancements in technology, increased competition, and innovative pricing models have made AI accessible and affordable for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Businesses that once viewed AI as a futuristic luxury can now leverage it to enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and gain a competitive edge. But what exactly has made AI more affordable for SMEs?
CLOUD COMPUTING AND AI AS A SERVICE (AIaaS)
One of the biggest barriers to AI adoption in the past was the high cost of computing power and infrastructure.
However, cloud computing has eliminated the need for SMEs to invest in expensive hardware and dedicated data centres. AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS) platforms, offered by providers like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, allow businesses to access AI tools on a pay-as-you-go basis.
This means SMEs can scale AI solutions according to their needs without upfront capital expenditure.
OPEN-SOURCE AI TOOLS
The rise of open-source AI frameworks such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn has significantly reduced the cost of AI development.
These tools are freely available, enabling SMEs to experiment with AI solutions without licensing fees.
Additionally, open-source communities provide extensive documentation and support, making AI more approachable for businesses with limited technical expertise.
AFFORDABLE NO-CODE AND LOW-CODE AI SOLUTIONS
Many SMEs lack in-house AI expertise, which historically meant hiring costly data scientists and developers.
Today, no-code and low-code AI platforms, such as Microsoft Power Automate, Google AutoML, and Bubble.io, empower businesses to build AI-driven applications without coding knowledge.
These solutions allow SMEs to implement AI-driven automation, analytics, and customer engagement tools without incurring high development costs.
ADVANCEMENTS IN AI HARDWARE AND PROCESSING EFFICIENCY
As AI algorithms have become more efficient, they require less computing power to run effectively.
AI models that once demanded high-performance servers can now operate on consumer-grade hardware or cloud-based virtual machines.
AI FOR BUSINESS AUTOMATION AND PRODUCTIVITY
AI-powered tools are now widely available to help SMEs automate repetitive tasks and streamline operations.
Chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated customer support platforms reduce the need for large customer service teams, lowering overhead costs.
AI-driven analytics tools enable SMEs to gain insights from data without expensive business intelligence (BI) software or specialised data analysts.
SUBSCRIPTION-BASED AI SOLUTIONS
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) business models have extended to AI, making it more affordable through monthly or annual subscriptions.
Businesses can subscribe to AI-powered CRM, marketing automation, and HR tools without investing in costly custom solutions.
Popular platforms like HubSpot, Zoho, and Salesforce now integrate AI-driven functionalities, offering SMEs advanced capabilities without excessive costs.
GROWING AI TALENT POOL AND OUTSOURCING OPTIONS
The rapid expansion of AI education and training has resulted in a growing pool of AI professionals available at competitive rates.
SMEs can now access freelance AI developers, consultants, and managed AI services from global marketplaces such as Upwork and Fiverr, reducing the need for full-time in-house specialists.
FINAL THOUGHTS
AI is no longer an inaccessible, expensive technology reserved for tech giants.
The convergence of cloud computing, open-source tools, no-code platforms, and subscription-based AI services has levelled the playing field for SMEs.
By embracing AI, SMEs can automate processes, improve customer experiences, and make data-driven decisions—all without breaking the bank.
Now is the time for SMEs to explore AI-driven opportunities and stay ahead in an increasingly competitive market.
AI for business development #7 - How AI grows your business (part 3)
AI drives business growth through various means, ranging from enhancing efficiency, creating
personalised customer experiences, fostering innovation, to expanding market opportunities. The
strategic use of AI varies by industry, but its transformative potential is evident across sectors.
Below are the key areas where AI contributes to growth.
6. PRODUCT AND SERVICE INNOVATION
AI fosters product and service innovation by enabling businesses to create new offerings, improve
existing ones, and enhance the development process itself. Here's a detailed exploration of how AI
drives innovation.
Accelerating research and development (R&D): AI algorithms process vast amounts of data to
identify patterns, simulate experiments, and predict outcomes. It reduces time-to-market for new
products and lowers R&D costs.
-e.g. In the pharmaceuticals industry, AI like DeepMind’s AlphaFold accelerates drug discovery by
predicting protein structures. In the materials science sector, AI identifies optimal material
properties for specific applications.
Personalised products and services: AI analyses customer data to develop products tailored to
individual preferences or needs. It increases customer satisfaction and loyalty.
-e.g. In healthcare, personalised medicine based on patient genetic data. In retail, custom-fit
clothing through apps like True Fit, using AI for body measurement analysis.
Predictive and adaptive features: AI-powered systems learn from user behaviour to predict needs
and adapt product functionalities in real time. It enhances user experience and product value.
-e.g. In the automotive industry, AI in smart cars learns driver preferences and adapts navigation or
climate settings. In consumer tech, AI in smartphones (e.g., Siri, Google Assistant) provides
personalised recommendations.
Smart products and IoT integration: AI combines with IoT devices to create intelligent, self-
optimising products. It adds functionality and convenience to everyday items.
-e.g. For home automation, AI-enabled smart thermostats like Nest learn and adjust to user
routines. For wearables, fitness trackers use AI to provide personalised health insights.
Prototyping and design optimisation: AI generates and tests product designs using simulations,
ensuring efficiency and cost-effectiveness. It accelerates product design and reduces prototyping
errors.
-e.g. In manufacturing, generative design tools like Autodesk Fusion 360 optimise product shapes
and materials. In fashion, AI predicts trends and assists in clothing design.
Enhanced customer feedback analysis: AI processes customer reviews, surveys, and social media
data to understand preferences and identify unmet needs. It provides insights to refine products
and develop new services.
-e.g. For consumer goods, AI tools like Brandwatch analyse customer sentiment for product
improvement. In travel and hospitality, hotels use AI to assess guest feedback and refine service
offerings.
AI as a core product: AI is developed as a standalone product or service offering, such as AI-
powered analytics or virtual assistants. It creates entirely new revenue streams.
-e.g. In software, AI platforms like ChatGPT offer conversational AI for businesses. For consulting
services, AI-driven data analysis services for industries like finance or healthcare.
Predictive maintenance and reliability: AI anticipates equipment failure or product degradation
based on usage patterns. It extends product life and enhances customer satisfaction.
-e.g. In aviation, AI predicts aircraft maintenance needs to prevent breakdowns. For appliances,
Smart washing machines use AI to monitor usage and notify users about maintenance.
Sustainability innovations: AI optimises resource use and helps design eco-friendly products or services. It supports green initiatives and reduces environmental impact.
-e.g. For energy, AI-powered systems like Siemens’ MindSphere optimise energy consumption. In packaging, AI designs biodegradable packaging materials.
Market trend prediction: AI analyses market data to identify emerging trends and customer demands. It helps companies stay ahead of competitors by offering innovative solutions aligned with market needs.
-e.g. For E-commerce, AI predicts future product categories with high demand. In media and entertainment, platforms like Spotify use AI to identify and promote trending music.
Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) innovations: AI powers immersive experiences, allowing customers to interact with products virtually. It enhances engagement and drives purchases in industries like retail and real estate.
-e.g. In furniture, IKEA’s Place app uses AR to visualise furniture in customers' homes. In real estate, virtual tours powered by AI help buyers explore properties remotely.
Automated testing and quality assurance: AI automates the testing process for products and services, ensuring quality and compliance. It reduces time and costs while maintaining high standards.
-e.g. In software development, AI-powered testing tools like Selenium detect and fix bugs efficiently. In manufacturing, AI-driven quality control systems inspect products for defects.
Enhancing product lifecycle management: AI monitors and manages every stage of the product lifecycle, from design to disposal. It optimises performance, updates features, and ensures sustainability.
-e.g. AI in consumer electronics updates software remotely for better functionality.
Cross-industry innovation: AI identifies transferable innovations from one industry to another. It encourages creative solutions and diversification.
-e.g. AI algorithms used in gaming (e.g. real-time decision-making) applied to autonomous vehicles.
In summary, AI enables businesses to innovate faster and smarter by optimising processes, predicting trends, and delivering personalised, adaptive, and sustainable products and services. This competitive edge allows organisations to stay relevant in rapidly evolving markets.
7. MARKET EXPANSION
AI helps businesses expand their market by identifying new opportunities, enhancing global outreach, optimising operations, and creating personalised customer experiences. Here's a detailed analysis of how AI drives market expansion.
Market research and analysis: AI processes vast amounts of market data, such as consumer behaviour, competitor performance, and economic trends, to uncover potential markets and niches. It provides actionable insights for entering untapped markets.
-e.g. AI tools like Tableau and Power BI analyse customer demographics to identify underserved regions. Predictive analytics forecast the success of launching products in new markets.
Customer segmentation and targeting: AI groups potential customers based on behaviour, preferences, and purchasing patterns, allowing businesses to target specific segments effectively. Tailored marketing efforts maximise engagement and conversion rates in new markets.
-e.g. E-commerce platforms like Shopify use AI to identify target audiences in international markets. Social media advertising platforms leverage AI for hyper-targeted ad campaigns.
Personalised marketing campaigns: AI analyses individual customer data to create personalised content, recommendations, and offers. It builds customer loyalty and drives conversions in new regions.
-e.g. AI-driven email marketing platforms like Mailchimp customise campaigns for local preferences. Recommendation engines in streaming services suggest culturally relevant content.
Language and cultural adaptation: AI-powered translation tools and localisation software adapt content to suit the language, culture, and preferences of new markets. It facilitates seamless communication and builds trust with local audiences.
-e.g. AI tools like Unbabel or Google Translate enable multilingual support and content adaptation. E-commerce platforms localise product descriptions and interfaces using AI.
Predicting market trends: AI predicts future trends by analysing data from social media, economic reports, and consumer behaviour. It helps businesses stay ahead of competitors and meet emerging demands in new markets.
-e.g. Retailers use AI to predict trending products in specific geographic regions. Travel companies forecast emerging tourist hotspots using AI.
Enhancing supply chain and logistics: AI optimises supply chain operations, including inventory management, transportation, and demand forecasting, ensuring efficient delivery to new markets. It reduces operational costs and ensures timely product availability.
-e.g. AI in platforms like IBM Watson Supply Chain predicts demand spikes in new locations. Logistics companies use AI for route optimisation to improve delivery efficiency.
Competitive analysis: AI monitors competitors’ activities, pricing, and strategies to help businesses position themselves effectively. It provides a strategic advantage by identifying gaps and opportunities in the market.
-e.g. AI tools like SEMrush analyse competitors’ marketing strategies in specific regions. Pricing algorithms adapt dynamically to remain competitive.
Reducing entry barriers: AI simplifies regulatory compliance, licensing, and other administrative tasks by analysing legal and market requirements. It speeds up market entry and reduces overhead costs.
-e.g. AI tools like Compliance.ai automate regulatory compliance processes for businesses entering foreign markets.
Building omnichannel presence: AI integrates data from online and offline channels to create a seamless customer experience. It increases brand visibility and enhances customer trust in new markets.
-e.g. Retailers use AI-driven tools to link e-commerce with physical stores. AI chatbots provide consistent support across platforms.
Risk mitigation: AI assesses risks such as market volatility, cultural challenges, or legal barriers and provides actionable recommendations to navigate them. It minimises potential losses and ensures smoother market entry.
-e.g. AI models predict economic stability and consumer purchasing power in target markets. Risk management tools like RiskWatch evaluate the feasibility of entering specific regions.
Identifying local partnerships: AI tools identify potential collaborators, distributors, or influencers who align with a company’s goals and values. It facilitates faster market penetration through trusted local networks.
-e.g. AI-powered LinkedIn Sales Navigator identifies regional distributors and partners. Social media platforms use AI to find influencers with high engagement in specific markets.
Leveraging emerging technologies: AI enables businesses to adopt innovative technologies like blockchain or IoT, giving them an edge in new markets. It enhances differentiation and appeals to tech-savvy customers.
-e.g. AI in IoT-powered smart devices caters to tech-conscious consumers. Blockchain-based solutions offer transparency and trust in markets with regulatory concerns.
Pricing optimisation: AI dynamically adjusts pricing strategies based on regional economic factors, customer purchasing power, and competitor prices. It ensures competitive pricing while maximising profitability.
-e.g. E-commerce platforms use AI to set region-specific prices. Hospitality companies like Airbnb use AI for dynamic pricing of accommodations.
Virtual assistance for customer engagement: AI chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 support in multiple languages, catering to diverse customer bases. It builds trust and enhances customer satisfaction in new markets.
-e.g. AI chatbots like Intercom assist customers with product inquiries in real time. Virtual assistants provide location-based recommendations.
Sustainability and ethical practices: AI helps businesses adopt sustainable practices, which are increasingly valued in global markets. It appeals to eco-conscious customers and aligns with local environmental regulations.
-e.g. AI monitors carbon footprints to meet regulatory requirements. Sustainable product design driven by AI resonates with global audiences.
In summary, AI empowers businesses to expand into new markets by enabling data-driven decision-making, personalisation, and operational efficiency. By leveraging AI, companies can identify growth opportunities, navigate cultural and regulatory complexities, and establish a strong presence in diverse regions.
AI for business development #6 - How AI grows your business (part 2)
AI drives business growth through various means, ranging from enhancing efficiency, creating
personalised customer experiences, fostering innovation, to expanding market opportunities. The
strategic use of AI varies by industry, but its transformative potential is evident across sectors.
Below are the key areas where AI contributes to growth.
4. AUTOMATE ROUTINE TASKS
AI automates routine tasks by leveraging machine learning, natural language processing (NLP),
robotic process automation (RPA), and advanced algorithms to handle repetitive and time-
consuming activities. This increases efficiency, reduces errors, and allows employees to focus on
strategic initiatives. Here’s a detailed overview of how AI automates routine tasks.
Data entry and management: AI tools extract, process, and input data from documents,
spreadsheets, and other sources into databases, and eliminate manual data entry errors and
speeds up data processing.
-e.g. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software like ABBYY automates invoice processing.
AI-powered CRM tools like Salesforce Einstein automate data capture from emails and calls.
Email sorting and responses: AI categorises incoming emails, flags important messages, and even
drafts or sends responses using NLP. It saves time and ensures prioritisation of critical
communications.
-e.g. Gmail’s AI-based Smart Reply suggests quick responses. AI customer service tools like
Zendesk handle email-based support tickets.
Scheduling and calendar management: AI analyses meeting requests, availability, and
preferences to schedule appointments or optimise calendars. It ultimately reduces back-and-forth
communication and optimises time management.
-e.g. Virtual assistants like Google Assistant and Microsoft Cortana automate meeting scheduling.
AI tools like Calendly manage and automate appointment booking.
Customer support: AI chatbots and virtual assistants respond to FAQs, guide users through
processes, and provide basic troubleshooting, offering 24/7 support and reducing the workload for
human agents.
-e.g. AI chatbots like Intercom and Drift automate customer interactions. Virtual agents in banking
guide users through tasks like balance inquiries and fund transfers.
Document processing and compliance: AI reviews and processes documents for errors,
formatting, and compliance requirements to reduce human involvement in tedious document
review tasks.
-e.g. AI platforms like DocuSign automate document signing workflows. Tools like Blue Prism
process legal and regulatory compliance forms.
Workflow automation: AI-powered RPA tools automate multi-step workflows, such as approvals,
reporting, and notifications. It enhances operational efficiency and ensures timely execution of
routine tasks.
-e.g. Tools like UiPath and Automation Anywhere automate invoice approvals and HR onboarding
processes.
Inventory management; AI automates stock tracking, replenishment, and forecasting based on
sales data and demand patterns. It reduces overstocking or stockouts and minimises manual
inventory checks.
-e.g. AI tools like IBM Watson Supply Chain optimise inventory levels. Amazon’s warehouses use AI to automate inventory management and fulfilment.
Payroll processing; AI automates payroll calculations, tax deductions, and payslip generation to reduce administrative burden and ensure compliance with payroll regulations.
-e.g. Payroll software like Gusto or QuickBooks uses AI to automate salary calculations and tax filings.
Data analysis and reporting; AI automates the aggregation, analysis, and visualisation of data for reports to provide real-time insights and reduce time spent on manual report generation.
-e.g. Business intelligence tools like Power BI and Tableau automate report creation. AI-driven insights in Google Analytics streamline web performance analysis.
Social media management; AI schedules posts, analyses engagement, and suggests optimal posting times, saving time and improves consistency in brand presence.
-e.g. Tools like Hootsuite and Buffer automate social media scheduling. AI algorithms provide content suggestions based on trending topics.
Recruitment and onboarding; AI screens CVs, schedules interviews, and provides new hires with onboarding resources. It speeds up hiring processes and ensures smoother onboarding experiences.
-e.g. AI in platforms like LinkedIn Talent Insights and HireVue automates candidate screening. Chatbots guide new employees through onboarding workflows.
Fraud detection: AI monitors transactions and flags unusual patterns for further review, reducing the time required for manual fraud checks while increasing accuracy.
-e.g. Banking AI systems like those used by PayPal and Visa automate fraud detection processes.
Financial forecasting and budgeting: AI analyses historical financial data to automate forecasting and budget preparation, It improves accuracy and eliminates the need for manual calculations.
-e.g. AI in tools like Anaplan automates financial planning. QuickBooks uses AI to predict future cash flow trends.
IT and system monitoring; AI continuously monitors systems for issues, automates backups, and resolves common IT problems, ultimately reducing system downtime and minimising the need for manual intervention.
-e.g. Tools like Splunk and Dynatrace use AI to automate system monitoring and alerting.
Content creation; AI generates content such as blog posts, product descriptions, or social media captions based on input parameters. it saves time for marketers and writers while maintaining quality.
-e.g. Tools like Jasper and ChatGPT create marketing content and ad copy. AI-generated personalised newsletters enhance customer engagement.
In summary, AI automates routine tasks across industries, from data processing and customer support to payroll and marketing. This allows businesses to streamline operations, reduce costs, and empower employees to focus on innovation and strategic goals.
5. EMPOWER WORKFORCE
AI empowers the workforce by enhancing productivity, enabling skill development, improving decision-making, and creating a more dynamic and adaptive work environment. Here's an in-depth look at how AI achieves this.
Automating routine tasks: by automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, AI frees employees to focus on more strategic and creative responsibilities. It increases job satisfaction and allows employees to apply their skills to higher-value work.
-e.g. HR: AI automates payroll and leave management. Marketing AI tools handle campaign scheduling and analytics.
Skill development and training: AI-driven learning platforms provide personalised training programmes based on employees’ roles, skills, and career aspirations. It accelerates upskilling and reskilling, ensuring employees stay relevant in a rapidly changing market.
-e.g. AI-powered platforms like Coursera or LinkedIn Learning recommend tailored courses. Virtual Reality (VR) simulations powered by AI provide hands-on training in fields like healthcare and manufacturing.
Real-time assistance: AI tools act as virtual assistants, providing employees with instant access to information, insights, or step-by-step guidance. It reduces delays, improves accuracy, and enhances confidence in task execution.
-e.g. AI-powered tools like Grammarly improve writing and communication quality. Sales assistants like Salesforce Einstein provide real-time insights into customer data during meetings.
Enhancing collaboration: AI optimises team workflows, schedules, and communication by analysing patterns and preferences. It improves team efficiency and reduces miscommunication.
-e.g. Tools like Microsoft Teams or Slack integrate AI for task management and scheduling. AI summarises meeting notes and action items automatically.
Data-driven decision-making: AI analyses large datasets and provides actionable insights, enabling employees to make informed decisions quickly. It reduces decision fatigue and increases confidence in outcomes.
-e.g. Finance teams use AI to forecast trends and optimise budgets. Marketing teams use AI to predict customer behaviour and refine campaigns.
Enhancing creativity and innovation: AI generates ideas, designs, and prototypes based on input parameters, sparking innovation and assisting in creative processes, expanding creative possibilities and reduces the time required for ideation.
-e.g. Designers use AI tools like Canva or Adobe Sensei for creative assistance. Writers use tools like Jasper or ChatGPT for drafting content.
Personalised support and well-being: AI monitors employee well-being and provides personalised support, such as reminders to take breaks or mental health resources. It promotes a healthier, more balanced work environment.
-e.g. AI tools like Workday measure employee engagement and suggest interventions. Wearable devices use AI to track stress levels and recommend relaxation techniques.
Predictive workforce management: AI predicts workforce needs, identifies skill gaps, and helps in workforce planning and optimisation. It ensures that employees are placed in roles where they can excel and contribute effectively.
-e.g. AI-powered workforce management tools like Kronos forecast staffing requirements. HR analytics platforms predict future hiring or training needs.
Improving accessibility: AI tools assist employees with disabilities by providing accessible technologies, such as text-to-speech, speech-to-text, or navigation aids. It creates an inclusive work environment and ensures equal opportunities.
-e.g. AI transcription services like Otter.ai assist hearing-impaired individuals. Text-to-speech tools like Read&Write support those with visual impairments.
Fostering employee autonomy: AI allows employees to self-manage tasks and workflows by providing intelligent tools that guide and optimise their activities. It encourages autonomy and reduces the need for constant supervision.
-e.g. AI-powered project management tools like Asana or Trello help employees prioritise and organise their workloads.
Enhancing customer interactions: AI equips employees with insights and recommendations to provide better customer service or close sales effectively. It empowers customer-facing teams to deliver personalised and impactful interactions.
-e.g. AI-driven CRM tools suggest personalised sales pitches or product recommendations. AI chatbots handle preliminary queries, enabling human agents to focus on complex issues.
Facilitating remote work: AI supports remote workers by ensuring seamless collaboration, monitoring productivity, and automating administrative tasks. It makes remote work more efficient and connected.
-e.g. AI tools like Zoom’s virtual background and noise cancellation features improve remote communication. AI-driven time trackers ensure accountability without micromanagement.
In summary, AI empowers the workforce by enhancing productivity, fostering innovation, and supporting employee well-being. By taking over routine tasks, providing real-time assistance, and enabling skill development, AI allows employees to focus on strategic and creative endeavours, making work more meaningful and impactful.
AI for business development #5 - How AI grows your business (part 1)
AI drives business growth through various means, ranging from enhancing efficiency, creating personalised customer experiences, fostering innovation, to expanding market opportunities. The strategic use of AI varies by industry, but its transformative potential is evident across sectors.
Below are the key areas where AI contributes to growth.
1. IMPROVED DECISION MAKING
AI significantly enhances decision-making by offering insights, reducing uncertainty, and enabling faster, data-driven choices. Here are the key ways in which AI improves decision-making across industries:
Data aggregation and integration: AI consolidates information from disparate sources such as databases, CRM systems, IoT devices, and social media. AI processes live data streams to provide timely insights, and decision-makers get a holistic view of their operations or market landscape.
-e.g. AI systems like Snowflake or BigQuery aggregate data from multiple channels for comprehensive analysis.
Advanced analytics: AI summarises historical data to explain past performance or trends. Machine learning models forecast future trends, such as customer behaviour or market demand (predictive analytics). and AI suggests the best course of action by evaluating possible outcomes (prescriptive analytics). Leaders can then anticipate challenges and opportunities with greater confidence.
-e.g. Retailers using predictive analytics to optimise inventory during seasonal peaks.
Pattern recognition: AI detects correlations and patterns in large datasets that humans might overlook to identify hidden trends. AI then flags anomalies in financial, operational, or market data, enabling swift corrective actions and providing informed decisions based on nuanced insights.
-e.g. AI in fraud detection identifies suspicious financial transactions in real time.
Scenario simulation: AI models simulate different What-If Analysis scenarios to assess the impact of potential decisions. AI quantifies the likelihood of risks and their consequences, aiding contingency planning, allowing leaders to make risk-aware decisions.
-e.g. AI-driven tools like Palantir simulate supply chain disruptions to optimise logistics strategies.
Decision automation: AI automates routine low-stakes decisions (e.g. email filtering or dynamic pricing), and for complex decisions, AI provides recommendations for human review. This speeds up decision-making processes and reduces cognitive load.
-e.g. Financial institutions using AI for credit scoring automate loan approvals for low-risk applicants.
Personalised recommendations: AI tailors recommendations based on customer preferences and behaviour (customer insights). AI tools also provide operational recommendations and suggest best practices for improving efficiency or profitability, adding precision in decision-making tailored to specific circumstances or individuals.
-e.g. E-commerce platforms like Amazon use AI to personalise shopping experiences.
Sentiment and market analysis: AI analyses customer reviews, social media posts, and news to gauge public sentiment (text mining). AI monitors competitors’ activities and market shifts (competitive analysis). Business leaders gain actionable insights into customer and market perceptions.
-e.g. AI tools like Brandwatch track brand sentiment in real time.
Bias reduction: AI minimises human cognitive biases by relying on data-driven insights (objective analysis). AI can audit decision-making processes to ensure inclusivity and enhanced fairness. Decisions are more equitable and grounded in facts.
-e.g. HR platforms like HireVue use AI to screen candidates based on objective criteria, reducing bias in hiring.
Time efficiency: AI performs complex computations much faster than humans (rapid analysis), and works around the clock, enabling 24/7 decision-making support (continuous operation) permitting faster decisions in critical situations.
-e.g. Emergency response systems using AI to prioritise resource allocation during crises.
Visualisation tools: AI creates dynamic, visually engaging intuituve dashboards that present key metrics and trends. AI highlights key insights in a narrative format, making them accessible to non-technical stakeholders (data storytelling). AI simplifies complex data for better understanding and actionability.
-e.g. AI in tools like Tableau enhances decision-making with data visualisation.
In summary, AI empowers organisations to make more informed, accurate, and timely decisions by leveraging data analysis, forecasting, and automation. By reducing uncertainty and enabling risk-aware strategies, AI transforms decision-making into a competitive advantage.
2. PERSONALISED CUSTOMER SERVICE
AI personalises the customer experience by leveraging data, machine learning, and predictive analytics to deliver tailored interactions, products, and services. Here's how AI achieves this.
Personalised recommendation: AI analyses customer data (e.g. past purchases, browsing behaviour, and preferences) to suggest relevant products or services, and increase customer satisfaction and conversion rates.
-e.g. E-commerce platforms like Amazon recommend products based on shopping history. Entertainment companies like Netflix uses AI to suggest shows and movies.
Dynamic content personalisation: AI customises website or app content based on individual user profiles, preferences, or geographic location, and provides a unique user experience that matches customer expectations.
-e.g. Retail websites displaying region-specific products or promotions. News apps recommending articles aligned with a user’s reading history.
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants: AI chatbots offer instant, personalised support by using customer data and natural language processing (NPL) to enhance customer service availability and reduces wait times.
-e.g. Banking chatbots provide account details and suggest financial services. In retail, assistants like IKEA's Anna guide users through online purchases.
Predictive customer insight: AI predicts customer behaviour (e.g. likelihood of purchase or churn) using historical data and machine learning models to enable proactive engagement to retain customers or close sales.
-e.g. Telecom companies using AI to identify customers at risk of switching providers and offering targeted retention deals.
Hyper-personalised marketing: AI refines marketing messages and campaign delivery based on customer preferences, timing, and behaviour, improving marketing ROI by reaching customers with the right message at the right time.
-e.g. Email marketing platforms like Mailchimp use AI to personalise email subject lines and content. Social media ads are tailored based on user engagement data.
Voice and speech recognition: AI-powered voice assistants (e.g. Alexa, Google Assistant) adapt to user preferences, such as favourite music, shopping habits, or frequently asked questions, providing a seamless and intuitive experience through conversational interaction.
-e.g. AI assistants suggesting playlists or managing smart home settings based on user preferences.
Sentiment analysis: AI analyses customer feedback, reviews, and social media to understand sentiment and preferences. Businesses can personalise responses and adjust offerings to align with customer emotions and expectations.
-e.g. AI-driven sentiment analysis tools helping customer service teams respond empathetically to negative reviews.
Behavioural retargeting: AI tracks online customer behaviour to serve relevant ads and reminders about abandoned carts or products of interest to increase engagement and reduces missed sales opportunities.
-e.g. AI-driven retargeting ads following up on items left in a shopping cart.
Real-time interaction and support: AI processes real-time data to adapt interactions, such as offering discounts when a customer hesitates at checkout, boosting sales and customer satisfaction with timely interventions.
-e.g. AI in mobile apps providing personalised fitness recommendations during workouts.
Personalised product or service design: AI uses customer input to design bespoke products or services, such as custom-fit clothing or personalised meal plans, delivering unique offerings tailored to individual needs.
-e.g. Nike’s app uses AI to measure foot size for custom-fit trainers. Health apps providing personalised diet plans based on user health data.
Loyalty and rewards programmes: AI analyses customer behaviour to tailor loyalty programmes, such as recommending rewards that align with past purchases to improve engagement and long-term retention.
-e.g. Starbucks’ AI-powered rewards app suggests customised offers to increase purchases.
Multilingual and cultural adaptation: AI translates and adapts content to cater to customers from different linguistic or cultural backgrounds, expanding market reach and ensures inclusivity.
-e.g. AI tools like Google Translate enable global businesses to localise content effectively.
Enhanced in-store experience: AI integrates with in-store systems (e.g., beacons or facial recognition) to personalise the physical shopping experience and combines online and offline data for seamless omnichannel experiences.
-e.g. AI recommending in-store promotions based on past purchases.
In summary, AI enhances customer personalisation by analysing individual preferences and behaviours to deliver meaningful and tailored experiences. Its ability to predict needs, automate support, and optimise interactions ensures customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3. ENHANCED SALES AND MARKETING
AI significantly enhances sales and marketing by improving efficiency, targeting accuracy, and campaign outcomes. Here’s an in-depth exploration of how AI can transform these functions.
Lead scoring and prioritisation: AI analyses customer data (e.g. demographics, behaviour, and engagement history) to rank leads based on their likelihood to convert. Sales teams can focus their efforts on high-potential prospects, increasing efficiency and conversions.
-e.g. Salesforce’s Einstein AI provides predictive lead scoring to prioritise sales efforts.
Personalised marketing campaigns: AI tailors marketing messages and campaigns based on customer preferences, behaviour, and purchase history to improve engagement and conversion rates by delivering relevant content to each customer.
-e.g. Email marketing platforms like Mailchimp use AI to personalise subject lines, sending times, and content. Spotify’s AI-driven personalised playlists (e.g. Discover Weekly) strengthen user engagement.
Predictive analytics for sales forecasting: AI uses historical sales data and market trends to predict future sales performance and demand patterns, enabling better resource allocation, inventory management, and strategic planning.
-e.g. Retailers using AI to forecast seasonal product demand and adjust stock levels accordingly.
Dynamic pricing: AI adjusts product prices in real-time based on factors like demand, competitor pricing, and customer willingness to pay to maximise revenue while remaining competitive in the market.
-e.g. E-commerce platforms like Amazon use dynamic pricing algorithms to optimise sales.
Customer segmentation: AI segments customers into highly specific groups based on behavioural, demographic, and psychographic data. Marketers can create tailored strategies for each segment, improving campaign relevance and effectiveness.
-e.g. AI-driven segmentation in tools like Adobe Experience Cloud enables hyper-targeted advertising.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI-powered chatbots handle customer inquiries, provide product recommendations, and assist with purchasing decisions. It enhances customer experience while freeing up human agents for complex tasks.
-e.g. Retail: AI chatbots help users find products or answer FAQs. B2B: Chatbots assist with lead qualification.
Enhanced customer insights: AI analyses customer behaviour across channels to provide deeper insights into preferences and buying patterns, informing both marketing strategies and product development.
-e.g. Google Analytics AI features highlight trends and anomalies in customer engagement. Shopify’s AI-powered tools provide insights into sales trends and customer preferences.
Marketing automation: AI automates repetitive marketing tasks such as email campaigns, social media posting, and A/B testing. It saves time and ensures consistent execution.
-e.g. HubSpot’s AI tools automate workflows, freeing marketers to focus on creative tasks.
Content optimisation: AI optimises content for SEO, readability, and engagement by analysing audience behaviour and trends, and ultimately increases content visibility and impact.
-e.g. Tools like Grammarly and MarketMuse provide AI-driven content recommendations.
Sentiment analysis: AI evaluates customer feedback, social media posts, and reviews to gauge sentiment towards a brand or product to help marketers adjust messaging and address concerns proactively.
-e.g. Social listening tools like Brandwatch analyse customer sentiment to guide campaigns.
Programmatic advertising: AI automates the buying and placement of ads, targeting audiences based on real-time data to increase ROI by serving ads to the most relevant audiences at optimal times.
-e.g. Google Ads uses AI to optimise bidding strategies and ad placements.
Sales enablement tools: AI equips sales teams with insights and tools to close deals, such as real-time customer data and personalised sales pitches. It enhances productivity and effectiveness of sales teams.
-e.g. LinkedIn Sales Navigator uses AI to suggest connections and provide actionable insights.
Enhanced lead nurturing: AI analyses customer interactions to personalise follow-ups and recommend the next best action in the sales journey, building stronger relationships and moves leads closer to conversion.
-e.g. CRM platforms like Zoho use AI to suggest personalised email content for nurturing leads.
Cross-selling and upselling: AI identifies opportunities to recommend complementary products or premium options based on purchase history to increase average order value and customer lifetime value.
-e.g. Retail: Amazon’s “frequently bought together” feature. SaaS: AI recommending advanced software features to existing customers.
Voice search optimisation: AI adapts marketing strategies for voice-based search queries through tools like NLP, and improves visibility in a growing search channel.
-e.g. Optimising content for voice search on smart assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant.
Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR): AI enhances VR/AR experiences for customers, such as virtual product try-ons or interactive ads to engage customers through immersive experiences.
-e.g. Sephora’s AR-powered app allows customers to virtually try on makeup
.
Continuous learning and optimisation: AI continuously analyses the performance of sales and marketing campaigns, making recommendations for improvement, ensuring strategies stay relevant and effective over time.
-e.g. AI in platforms like Optimizely provides real-time recommendations for A/B testing results.
In summary, AI transforms sales and marketing by automating tasks, improving targeting, and enhancing personalisation. The result is a more efficient process that drives higher ROI, better customer experiences, and stronger brand loyalty.
AI for business development #6 - How AI grows your business (part 2) will explore other growth opportunities such as Product and Service Innovation, Market Expansion, Risk management and Workforce Empowerment.
AI for business development #4 - Generative AI
Benefits of Generative AI
Generative AI brings significant advantages, making it a transformative force in technology and business.
- Creativity and innovation: enables the creation of unique content, designs, and solutions.
- Automation and efficiency: reduces time spent on repetitive tasks, allowing teams to focus on strategy and innovation.
- Personalisation: delivers customised experiences, from product recommendations to targeted marketing.
- Enhanced decision-making: provides insights by simulating potential scenarios or generating analytical reports.
- R&D Support: accelerates product development by testing ideas through simulations and AI-driven innovation.
- Economic opportunities: unlocks new revenue streams and business models, fostering competitive advantages.
UNLOCK OPPORTUNITIES WITH GENERATIVE AI
Generative AI presents a wealth of opportunities to transform and optimise your business. As you embark on implementing AI within your organisation, there are several avenues you can explore.
1. Leverage existing market tools
Use readily available AI tools to perform specific tasks, such as capturing meeting minutes, generating presentations, creating social media content, summarising documents, conducting quick information searches, and more.
These tools are:
- User-friendly: minimal learning curve,
- Quick to implement: no complex setups required,
- Cost-effective: affordable for businesses of any size,
- Efficient: save significant time while boosting productivity.
2. Upgrade your existing systems
Enhance your current systems (e.g., MRP, CRM) by adopting the latest AI features offered by your providers. For example, CRM platforms now use AI to gather client intelligence, streamline email workflows, manage leads, organise tasks, and automate processes.
This approach offers:
- Improved efficiency: optimises operations without disrupting your organisation’s structure,
- Smooth evolution: gradual upgrades to familiar tools enhance functionality without requiring major changes.
3. Create custom AI agents
Develop AI agents tailored to your business needs to automate tasks, research and identify sales leads, build customer service interfaces, such as chatbots and virtual assistants, and more.
Key benefits include:
- Ease of use: many no-code or low-code platforms are available,
- Affordability: running costs are generally low,
- Customisation: aligns with your specific business requirements.
While this option involves some effort to develop and implement, the value it brings to your operations can be significant.
4. Build bespoke AI solutions
Integrate custom AI solutions directly into your business processes to achieve:
- Enhanced efficiency: automate complex workflows and improve decision-making,
- Tailored optimisation: solutions uniquely designed for your company’s needs.
This option is ideal for businesses seeking a competitive edge or looking to innovate at scale.
5. Incorporate AI into your products and services
Integrate AI features into your products or services to improve existing offerings, or introduce innovative new solutions to the market.
This approach not only enhances customer experience but also positions your business as a leader in AI-driven innovation.
Strategic considerations for advanced AI initiatives
Starting with readily available tools provides immediate benefits with minimal investment, making AI accessible even to small and medium enterprises.
Over time, you can evolve to more advanced applications, such as custom AI solutions or integrating AI into their products and services. While these require higher investment and time, the potential returns in efficiency, innovation, and market leadership make it worthwhile.
Generative AI is no longer a distant future—it’s here, transforming industries and empowering organisations to think bigger and bolder.
If you decide to pursue the more advanced options (4 and 5), it’s essential to align your AI plans with your overall business strategy. Consider the following:
- Define clear objectives: Ensure your AI initiatives support your company’s long-term goals.
- Assess resource needs: Availability of data, time, and funding is critical.
- Build expertise: Leverage internal talent or seek external expert support to guide development and integration.
While these approaches may require significant investment in terms of resources and effort, the potential for increased efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness makes them highly worthwhile.
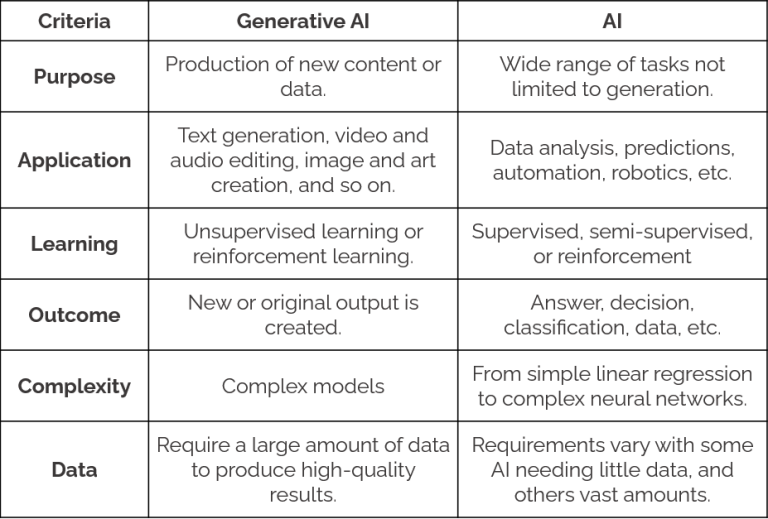
Generative AI is a groundbreaking subset of machine learning that focuses on creating new
content — ranging from text, images, and videos to music and even 3D models.
Unlike traditional AI, which primarily analyses data to make predictions or classifications,
generative AI produces entirely new and original data that mirrors the patterns and characteristics
of the training data.
Using advanced neural networks, generative AI models are trained on vast datasets, often
employing unsupervised or semi-supervised learning techniques. This enables them to learn from
unlabelled data and generate creative outputs that can mimic, enhance, or innovate on existing
styles and formats.
How does Generative AI work?
Generative AI relies on models trained to detect patterns and structures within data. When
prompted, these models create content by extrapolating from what they’ve learned.
A critical component of this process is prompt engineering, where users craft specific instructions
(or prompts) that guide the model’s output. A well-structured prompt can significantly influence
the quality and relevance of the generated content.
Examples of Generative AI models
The technology landscape is teeming with generative AI models from leading tech companies.
Here are some prominent examples:
- OpenAI ChatGPT: excels in generating human-like text for content creation, conversation,
and more. - Google Gemini: qn AI powerhouse with capabilities in text, image, and multimodal
applications. - Meta Llama: focuses on scalable, efficient AI solutions.
- Anthropic Claude: known for safe, explainable AI interactions.
These tools represent just a fraction of the expansive and ever-growing ecosystem of generative
AI.
Applications of Generative AI
Generative AI has revolutionised countless domains by offering innovative solutions.
Text:
- Content creation for blogs, social media, and marketing.
- Summarising lengthy documents.
- Code generation for developers.
- Language translation for breaking linguistic barriers.
Art, image, and video:
- Creating and editing images, videos, and animations.
- Enhancing photos or generating realistic visuals for design and branding.
Music:
- Composing original music.
- Automating podcast creation or editing.
Business:
- Automating customer service with chatbots and virtual assistants.
- Personalising marketing campaigns.
- Designing visually compelling presentations.
Generative AI vs Traditional AI
While traditional AI focuses on recognising patterns, making predictions, or classifying data, generative AI thrives in creation. Its ability to generate original, high-quality content opens doors to unparalleled creativity and innovation across industries.
AI for business development #3 - Machine Learning
Machine learning is a transformative branch of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that focuses on enabling
computers to perform tasks by learning from data instead of following explicitly programmed
instructions.
Unlike traditional rule-based AI systems, machine learning models identify patterns in historical
data and use these insights to make predictions or decisions. This adaptability makes ML a
cornerstone of modern AI applications.
Supervised Learning: Learning from Labels
Supervised learning is a type of ML where models are trained on labelled data. Each data point
includes an input and an associated output, allowing the model to discover relationships between
the two. Once trained, the model can predict or classify new, unseen data with confidence.
Applications of Supervised Learning
- Email and chat classification automatically sorting emails into spam and non-spam
categories or categorising customer queries.
- Language translation powering tools to convert text from one language to another.
- Quality control inspecting manufacturing products for defects.
- Product recommendation suggesting items based on past user behaviours.
- Demand forecasting predicting future customer demand to optimise inventory.
- Predictive maintenance monitoring machinery to preemptively address issues before
breakdowns.
- Virtual assistants enabling intelligent interactions with AI-driven assistants like Siri or Alexa.
- And so many more.
Unsupervised Learning: Finding Hidden Patterns
In contrast to supervised learning, unsupervised learning deals with unlabelled data. Models
autonomously explore and uncover hidden structures, relationships, or clusters within the dataset.
Applications of Unsupervised Learning
- Customer segmentation grouping customers based on purchasing behaviour to tailor
marketing campaigns.
- Anomaly detection identifying unusual activities in cybersecurity or financial transactions.
- Market analysis recognising trends and shifts in market dynamics.
- Social network analysis mapping connections and influencers in a social media network.
- Document clustering organising vast collections of text into meaningful groups.
- Supply chain management optimising inventory and logistics.
- Workflow optimisation streamlining processes for increased efficiency.
- And so many more.
Reinforcement Learning: Learning by Doing
Reinforcement learning involves an agent interacting with an environment, making decisions, and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. Over time, the agent refines its actions to maximise rewards.
Applications of Reinforcement Learning
- Production line optimisation enhancing efficiency in manufacturing workflows.
- Warehouse management automating warehouse operations, such as sorting and inventory handling.
- Dynamic pricing adjusting prices based on supply and demand.
- Energy management systems reducing energy usage through optimised scheduling.
- Autonomous robot control teaching robots to perform tasks like assembly or navigation.
- Financial portfolio optimisation improving investment strategies.
- Delivery route optimisation ensuring timely deliveries by finding the most efficient paths.
- And so many more.
Neural Networks and Deep Learning: Mimicking the Brain
Neural networks are computational models inspired by the human brain. They consist of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process data and learn patterns. When scaled to many layers, they form the foundation of deep learning, which excels at analysing large datasets.
Deep Learning Applications
- Image recognition identifying faces, objects, or scenes in photos.
- Computer vision enabling technologies like self-driving cars to "see" and interpret their surroundings.
- Natural language processing (NLP) powering AI to understand and generate human language.
- Speech recognition converting spoken words into text, as used in virtual assistants.
- Autonomous vehicles facilitating real-time decision-making for safe navigation.
- Content generation creating images, text, and audio using generative AI.
- And so many more.
PREPARING YOUR ORGANISATION FOR MACHINE LEARNING
To successfully adopt machine learning, organisations must focus on the following:
- Data readiness: organise existing datasets or acquire new ones relevant to your objectives.
- Define objectives: clearly outline both short- and long-term goals for AI integration.
- Adopt cost-effective tools to foster an AI culture: introduce simple AI applications to build confidence and familiarity across teams.
For example, start with accessible solutions like:- Dicte.ai and Eric.ai for meeting transcription and minutes.
- Gamma for creating presentations.
- Canva for producing visual content.
- Strategise for the future: lay the groundwork for ambitious AI implementations by aligning efforts with a robust, long-term AI strategy.
ML opens a world of possibilities for businesses, empowering them to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and unlock new opportunities. By taking small, thoughtful steps today, organisations can set themselves on a path to long-term success in the AI-driven future.
AI for business development #2 - Rule-based AI
Rule-based AI systems represent the foundation of artificial intelligence by operating through predefined rules to process input data and produce decisions or outcomes. These rules are often structured as simple "if-then" statements, such as:
- If the temperature exceeds 30°C, then turn on the cooling system.
This deterministic nature ensures that the system produces consistent results for the same input, as long as the rules remain unchanged.
By embedding the knowledge and skills of experts into a software model, rule-based AI eliminates the need for large datasets or extensive computational training.
Rule-based AI techniques are straightforward, interpretable, and reliable for domains with well-defined logic or where decisions must adhere to strict rules.
Advantages of Rule-Based AI
Rule-based systems excel in scenarios where logic is clear, and decisions must be transparent. Their benefits include:
Cost-effectiveness
- No need for extensive datasets or expensive hardware.
- Easily accessible for organisations with limited AI resources.
Simplicity
- Rules are easy to create, modify, and comprehend.
- Ideal for domains where decisions follow fixed criteria.
Transparency
- Decision-making processes are entirely explainable.
- Traceable rules ensure trust in the system's outputs.
Rapid deployment
- Quick to implement with minimal setup.
- Seamlessly integrates into existing workflows.
Limitations of Rule-Based AI
While rule-based AI has its strengths, it is less suitable for dynamic or complex scenarios due to:
Limited adaptability: unable to adjust to new or ambiguous conditions without manual updates.
Scalability issue: managing thousands of rules can become increasingly complicated.
Dependency on experts: requires domain specialists to define accurate rules.
Maintenance overhead: rules need frequent updates to reflect changing conditions or requirements.
APPLICATIONS OF RULE-BASED AI
Rule-based AI has found its way into various industries, powering systems that simplify repetitive and logical tasks.
You might be using AI for quite some time
without even knowing it.
Here are some examples among many others:
Business operations
- Invoice approval automates processes with rules like: approve if the amount is below £10,000 and matches a purchase order.
- Loan assessments with decisions based on parameters such as credit scores and income-to-loan ratios.
Manufacturing
- Automated machinery adjusts settings with rules like: increase conveyor speed if production demand rises.
- Defect detection identifies quality issues based on predefined patterns or tolerance thresholds.
Retail
- Product suggestions suggests items such as: if a customer buys a mobile phone, offer phone cases or screen protectors.
- Stock management automatically reorders inventory when stock levels fall below a set threshold.
Customer Interaction
- Rule-based chatbots respond to inquiries with structured, rule-driven workflows.
Tax and compliance
- Tax filing software automates calculations using specific tax laws and pre-established conditions.
Everyday examples you may already use
Many of us interact with rule-based AI daily, often without realising it:
- Spam filters: email systems use rules like: mark as spam if certain keywords are detected or the sender is unverified.
- Automated adjustments: home thermostats adjust heating or cooling based on predefined temperature rules.
GETTING STARTED WITH RULE-BASED AI IN YOUR ORGANISATION
Implementing rule-based AI can be a cost-effective and straightforward way to introduce automation. Start small:
- Identify opportunities: look for repetitive, rule-driven tasks in your workflows that can benefit from automation.
- Pilot in low-risk areas: test rule-based solutions in processes with a high return on investment (ROI), like invoicing or inventory management.
- Leverage existing resources: utilise your team’s domain knowledge and internal IT capabilities, avoiding the need for AI experts.
By focusing on these initial steps, organisations can gain confidence in AI technologies and set the stage for future advancements.
AI for business development #1 - What is AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an evolving branch of computer science that aims to replicate human
intelligence within machines. It involves creating algorithms and systems capable of performing
tasks that traditionally required human cognitive abilities.
These tasks include reasoning, learning, problem-solving, prediction, perception, automation,
and understanding language.
AI has fundamentally transformed industries, from healthcare and finance to education and
entertainment, by enabling machines to handle complex data-driven tasks with remarkable
accuracy and efficiency.
Narrow AI: Specialised Brilliance
Often referred to as Weak AI, Narrow AI systems are designed to perform specific tasks or a
limited set of functions with exceptional proficiency. They do not possess general intelligence and
cannot adapt their capabilities beyond their defined domain.
Despite these limitations, Narrow AI has revolutionised everyday applications.
Examples of Narrow AI:
- Voice assistants help with tasks like setting reminders, answering questions, or controlling
smart devices.
- Recommendation systems used by streaming plateforms to suggest personalised content
or by ecommerce websites to suggest products.
- Image and facial recognition AI algorithms identify individuals or objects in photos and
videos, widely used in security and social media.
- Fraud detection systems used by financial institutions to identify and prevent fraudulent
transactions.
- Chatbots and customer support systems enhance user experiences with 24/7 automated
assistance.
- Medical imaging AI aids to diagnose diseases by analysing radiology scans.
- Language translation
- Robotic process automation (RPA)
General AI: The Vision of Human-Like Intelligence
Also known as Strong AI, General AI refers to systems with the capability to perform a broad
spectrum of intellectual tasks. These systems can learn, understand, and apply knowledge
across various domains, demonstrating cognitive abilities akin to human intelligence.
While true General AI remains a future aspiration, some technologies hint at its potential:
- GPT language models like ChatGPT simulate human-like text generation and problem-
solving.
- Advanced robotics and self-driving cars showcase adaptability in dynamic and
unpredictable environments.
Super AI
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI), is a hypothetical form of artificial intelligence that would
surpass human intelligence in all respects, including creativity, problem-solving, social skills,
and general knowledge.
TYPES OF AI SYSTEMS
AI systems can range from basic rule-based programs to advanced neural networks and deep learning models capable of analysing complex patterns in data, making predictions, and improving their performance over time through learning.
Traditional AI (rule-based AI)
Involves programming explicit rules for the AI system to make decisions.
- Rule-based (expert) systems encode experts’ knowledge and skills into a software-based model.
- Converts conditions into a series of if/then rules.
- No data is needed.
While straightforward, these systems lack the ability to learn or adapt over time.
Machine Learning (ML)
A subfield of AI that is focused on getting computers to learn without explicit programming and make decisions based on data.
- Supervised learning models are trained on labelled data.
- Unsupervised learning models find patterns in unlabelled data.
- Reinforcement learning systems learn by interacting with their environment and receiving feedback.
- Deep Learning utilises neural networks to analyse vast amounts of data and make complex predictions.
PRACTICAL STEPS TO AI ADOPTION
A first step simple and cost-effective approach to introducing AI into your organisation is to equip your teams with tools like ChatGPT, Claude, or Gemini.
You will quickly enhance productivity through tasks like drafting emails, preparing and minuting meetings, searching information, solving problems, getting documents’ insights, creating content and so many more.
This step not only saves time and resources but also fosters an AI culture and encourages the adoption of AI within the organization.
Copyright © 2024 Winsales. All rights reserved.
Privacy Policy - Terms of Use - Legal Notice
We need your consent to load the translations
We use a third-party service to translate the website content that may collect data about your activity. Please review the details in the privacy policy and accept the service to view the translations.
